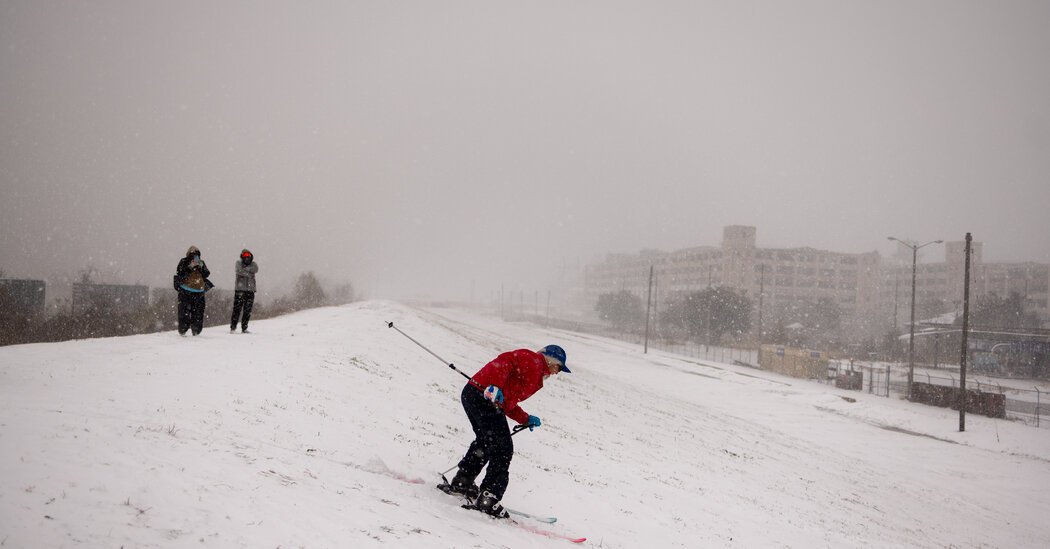
An unusual flurry of cold air down from the North Pole has prompted the first-ever blizzard warning for southern Louisiana and grounded flights in Houston. Cold weather could sweep the country this week with heavy snowfall from the Northeast to the Gulf Coast.
What is responsible for the sudden cold? Polar vortex. And it’s acting strangely because of climate change, although not all researchers agree.
A polar vortex is a large, rotating mass of cold air that typically extends over the Arctic. It becomes stronger in winter, when the Northern Hemisphere turns away from the Sun.
Normally, the polar jet stream, a band of strong winds that encircles the globe and blows from west to east, surrounds the vortex and keeps it in northern latitudes, areas that are more prone to cooler temperatures. are But when the jet stream sinks, cold air can escape and travel south.
Within hours, temperatures could drop into the tens of degrees and snow could hit parts of the United States, such as Florida and Texas, which are known for balmy weather. Cold air may persist until the Arctic vortex stabilizes again.
On a warming planet where rising temperatures are a key symptom of climate change, scientists agree that we will continue to see unusually cold temperatures. Oh 2021 study suggested that changes in the Arctic, which is warming twice as fast as the rest of the world, are expanding the polar vortex and further sinking the jet stream.
“Climate change has increased disruptions to the polar vortex,” said Juda Cohen, study author and an atmospheric scientist at Atmospheric Environmental Research, an environmental research consulting firm.
While cold cases in the United States have declined overall since the 1960s, Dr. Cohen argued in a statement. 2023 study That, since 2000, the frequency of cold air outbreaks has been increasing, but not yet enough to be considered a trend.
But research like Dr. Cohen’s continues.
“We just don’t see a strong increase in extreme cold events,” Zeke Hausfader, a climate scientist at Berkeley Earth, a research organization, said last week. “If anything, they’re decreasing.”
Snowfall is also expected to decrease tomorrow. “What we expect is that, as things get warmer, you can expect the total amount of ice to decrease over time,” said Gavin Schmidt, director of the NASA Goddard Institute for Space Studies. “
This week’s Arctic blast has highlighted the growing risks of falling temperatures, especially in regions unaccustomed to them. In the United States, deaths from cold weather have doubled in the past two decades. In 2022, more than 3,500 people died due to the cold. According to one study From the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
At least Two deaths from cold Already reported in Austin, Texas.