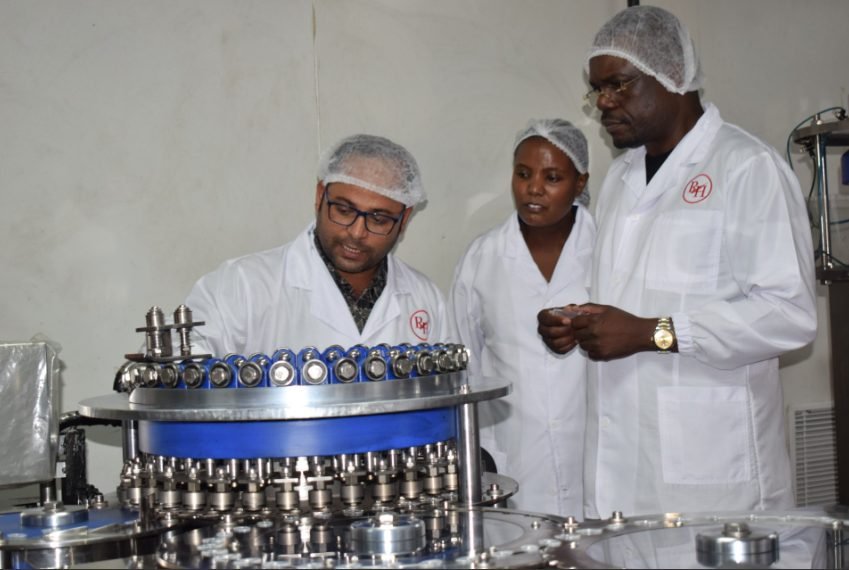
Development Finance (DFI) is moving forward to accelerate the ambitions of African pharmaceutical and vaccine manufacturing, which indicate a new phase under continental pressure for self -sufficiency in health products.
Funding proposals were presented during the 2th vaccine and Health Products Manufacturing Forum held in Cairo from February 4-6, 2025. The gathering with Africa CDC, Gavi, Vaccine Alliance, and regional vaccine manufacturing cooperation (RVMC), in which stakeholders made stakeholders as hosts.
African Export – Import Bank (AFPRACKS Bank,), including African Development Bank, European Investment Bank (EIB), World Bank, International Finance Corporation (IFC), and French Development Agency, to accelerate local pharmaceutical production and increase global health strategies for international health. He also highlighted the current and incoming investment of his institutions to support these efforts.
The Afrikam Bank outlined its progress in promising US $ 2 billion to help the manufacture of health care and health products. Meanwhile, companies like IFC and EIB have introduced new financing measures that they are preparing with partners.
This speed indicates a significant change in the journey toward Africa’s self -reliance, ensures sustainable manufacturing ecosystem, reduces dependence on external supply chains, and improves the preparation of pandemic diseases. The forum set up at the speed of the 2023 gathering in Morocco, Morocco, where 25 vaccine manufacturing measures were identified in the continent, which has 10 already existing capacity.
Delegates in Cairo also learned that Egypt has positioned itself as one of the latest African producers, offering a model to eliminate the continent’s manufacturing gap. What is possible when strong political will, strategic investment, and regulatory exchanges are exchanged?
Egypt’s progress is in line with the African Union’s purpose of producing 60 % of the vaccine locally by 2040. However, the purchase remains an important challenge. Egyptian Drug Authority Chairman, Dr. Eli al -Ghamravi, emphasized the dangers of external dependence: “Kovide -19 is a reminder of how Africa was pushed to the back of a row for life -saving medicines. We rely on the external suppliers at the time of crisis.
Egypt’s regulatory development has also established a new benchmark. In December 2024, the World Health Organization recognized the first African country to achieve maturity levels for medicines and vaccines-a milestone that indicates a well-organized and stable pharmaceutical sector. This success is with Egypt’s first locally manufactured insulin preparation.
Although Egypt’s progress is commendable, there are widespread challenges throughout the continent. The scattered regulatory system, limited technology, shortage of manpower, lack of off -tech guarantees, and financing differences have hindered regional manufacturing growth.
Talent Development Lead for the African CDC Platform for Harmonized African Health Manufacturing (PHAM) platform, Dr. Chileuba Moula emphasized the need for industry-acidium support to promote stem curriculum, internship, and employment training.
Despite these challenges, progress is underway. New financing mechanisms and policy shifts are behind the pace. In June 2024, Gavi launched the African vaccine manufacturing Axular (AVMA), which gained US $ 1.2 billion to increase vaccine production in Africa. At the same time, the African Bank promised US $ 2 billion under the Africa Health Security Investment Plan. The newly established African Polyes is ready to increase the assurance of demand and the market stability.
Meanwhile, the African Medicine Agency was highlighted as a prominent in the forum, participants emphasized on strong regulatory coordination to accelerate approval and ensure safety. The African Continental Free Trade Area was also recognized as the key to enhancing regional trade and strengthening market access.
Dr. Jane Kasia, Director General of the African CDC, confirmed the continent’s vision: “The agenda of local manufacturing is not an option. It is a vision we are preparing.
The new partnership announced at the forum highlighted Africa’s expansion capacity for vaccine, diagnosis and treatment. Afrjin and Biogenic Pharma advanced the transfer of MRNA technology, while Evarma, Quantom and Unizima reinforced mutual cooperation in the development of MRNA vaccine and promoting local manufacturing and relying on importing local manufacturing.
The 12 member countries participated in the forum (Algeria, Egypt, Ethiopia, Ghana, Kenya, Morocco, Nigeria, Rwanda, Senegal, South Africa, Uganda, and Zambia), national regulatory officials, regional economic community, African communities, global partners, global partners, global partners, global partners. Since Africa moves towards its goal of developing 60 % of its vaccine by 2040, it will be very important in achieving this vision with permanent investment, harmony rules, and the cross sector.