Sign up for CNN’s Wonder Theory Science Newsletter. Discover the universe with interesting discoveries, scientific advances and more related news.
Cnn
B (b (b (
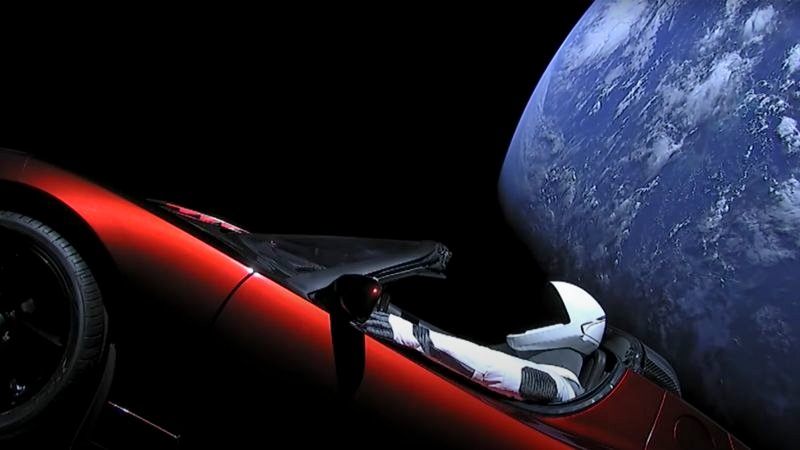
Seven years after Space X launched Elon Musk’s Cherry Red Sports Car into orbit around our sun, astronomers began to focus on its movement once again.
Observers Spotted and correctly identified The vehicle launched its extraordinary walk in February 2018 – after the Falcon heavy rocket was trapped in space during a speeding madman launch. But recently, the car created a high -level case of wrongdoing as space observers misunderstood it for Terdagra.
According to the International Astronomical Union’s modest planet center, numerous observations of the vehicle were inadvertently placed in a database for the vehicle through a clean survey of the night sky.
An amateur astronomer saw a string of data points in January, which was seen to fit together, which described the orbit of a relatively smallest small item that flocks between the orbit of the earth and Mars. It was
The urban scientist assumed that the mystery object is a non -documentary disciple and immediately sent its results to the MPC, which works at the Harvard Smithsonin Center for Astro Physics in Cambridge, Massachusetts, of a clearing house. As such, it tries to categorize all the famous temptations, comeds and other smaller selasts. The bodies were confirmed by a astronomer there.
And so, the center of the slightest planet logged in a new item, a new “CN41”.
However, within 24 hours, the center withdrew office.
MPC astronomer Peter Verus told CNN that the person who actually flagged the item realized his mistake, and seeing that he was actually found several unrelated observations of Musk’s car. Yes. And the center system did not catch the error.
“(Astronomer) was correct. (Data points) was really together, “Wares said, who made a database entry for CN41.” But once again, we only get numbers.
Verus added, “So from this point of view, if you do not know, this is Tesla Roadter, then there is no way to tell.”
This was a significant issue of wrongdoing. But it was already far away, because in similar cases astronomers have to suffer. Mixups highlight the difficulties of tracking items in the deep space.
NASA Paul Chaudas withdrew CNN. Chaudas is the director of the Center for Earth Object Studies at the Jet Propulsion Laboratory in California, California.
Space experts had mistaken a rocket body on a collision with the moon for the moon for the Space X -launch vehicle before being confirmed by one of China’s past lunar missions.
A piece of Apollo 12 Mission’s Saturn V rocketWhich picked up three astronauts on the other The moon landing was surprised by the scientists in the early 1969, when the Earth returned to the orbit of the Earth. Astronomers had to closely examine the strange and strange pace of wasted hardware to make an accurate identity.
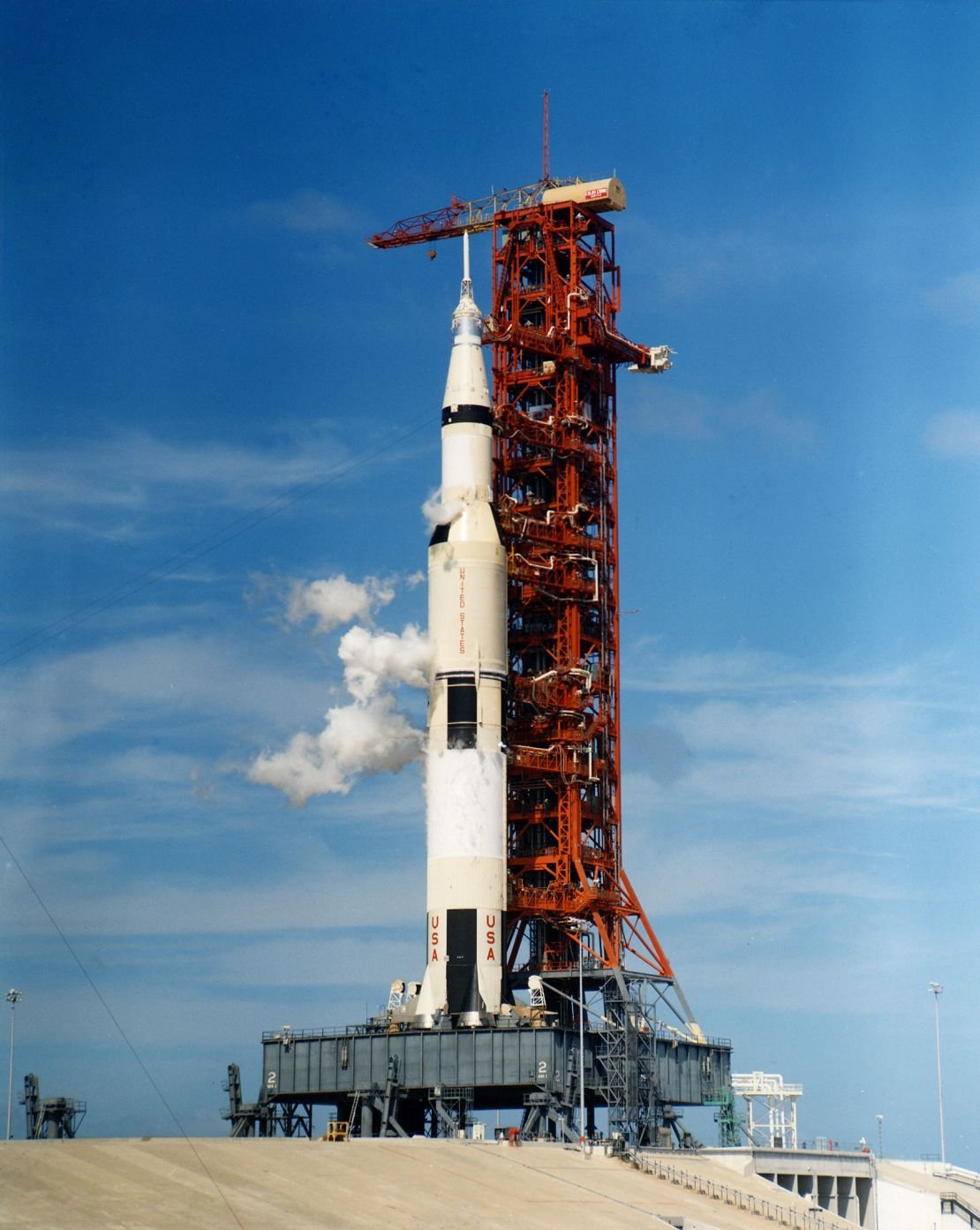
University of Hawaii Pan Stars 1 telescope saw another rocket part in 2020, which helped NASA be ruined. Surveyor 2 lunar Investigation During the rise of the 20th century space race in 1966. Chaudas said the researchers were confused until the US government ordered the “high -level Bank Agency” attempt to find out what was known.
Interested in understanding and tracking deep space items, and sometimes in a hurry, a desire to basically understand the works of the universe, as well as help policy makers and scientists understand the threats-they are the dangers. Whether it is a temptation or foreign opponents.
Mask’s sports car managed to withdraw from professionals in our solar system for a number of reasons.
An important factor: Experts are not interested in having a tab on the car.
The car is not on the pursuit of scientific pursuit. It was sent into space as a piece of deadweight in the opening test of SpaceX’s Falcon Heavy rocket, and now the destiny of the vehicle is to spend forever in our universe neighborhood.
The car is a very small opportunity to ever affect the ground. As far as astronomers are concerned, it is just a heavy piece of space trash.
Nevertheless, misunderstanding a spacecraft or human -made item for a temptation is a problem for the center of the minor planet, which is only given the task of identifying naturally found.
“We do not want to receive (data) about any artificial objects,” said Verus, adding to the MPC, “This is basically waste for us.”
The center is working with the NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory to improve the data from the agency’s horizon system database, which holds the closest tabs on the potentially dangerous temptation on space cliffs and flags.
Verus said he has written a code aimed at better scanning human -made items that can slip through the NASA horizon database and slip through the filters of the slightest planet. Chodas said it was implemented this week.
If this adjustment was made earlier, he added, patch Almost definitely the error must have been caught.
Nevertheless, Weres added, updating the code is not a resolution.
“This is still not a bulletproof, and this problem is the number of new launches of spacecraft,” he said.
He said that today, the world of space flights is as driven by the business industry as it is by government agencies like NASA. And private companies are not always transparent about where they send them into space. This one problem is that of the fact that companies are launching more often than public space programs.
For example, Space X launched about 140 140 rockets in just 2024-a more than 30-year space shuttle program was launched.
Wars noted that this problem is not just about the satellite and spacecraft, but the rocket parts that are occasionally trapped in the valley after ending the mission.
Although both JPL and MPC focus on listing and tracking of natural discourse, doubles and other natural bodies, the day will come when the astronomers also have human-made items in deep space. You have to start to look closely.
He said, right now, Chodas estimates that there are about 100 human -made things in orbit around the sun, and “most of those things are wasted because they are not much detected.”
“The most important thing is: The orbit of these items around the sun has no reliable database.”
Lack of data can be a problem, as increasing traffic experts can put sludge about astronomy and complicate the work of tensions that can invade the ground.
Verus added, “I think this topic will be more important in the coming years.
In a case: Estrophore Huntington Beach, a California, is a bold start, aimed at one day in the deep place my rare metals. The company plans to launch a small spacecraft named Odin in late February, to fly through a scream and snap images to investigate its surface.
For the first time in this mission, a private company has sent a spacecraft a deep place, or out of the moon.
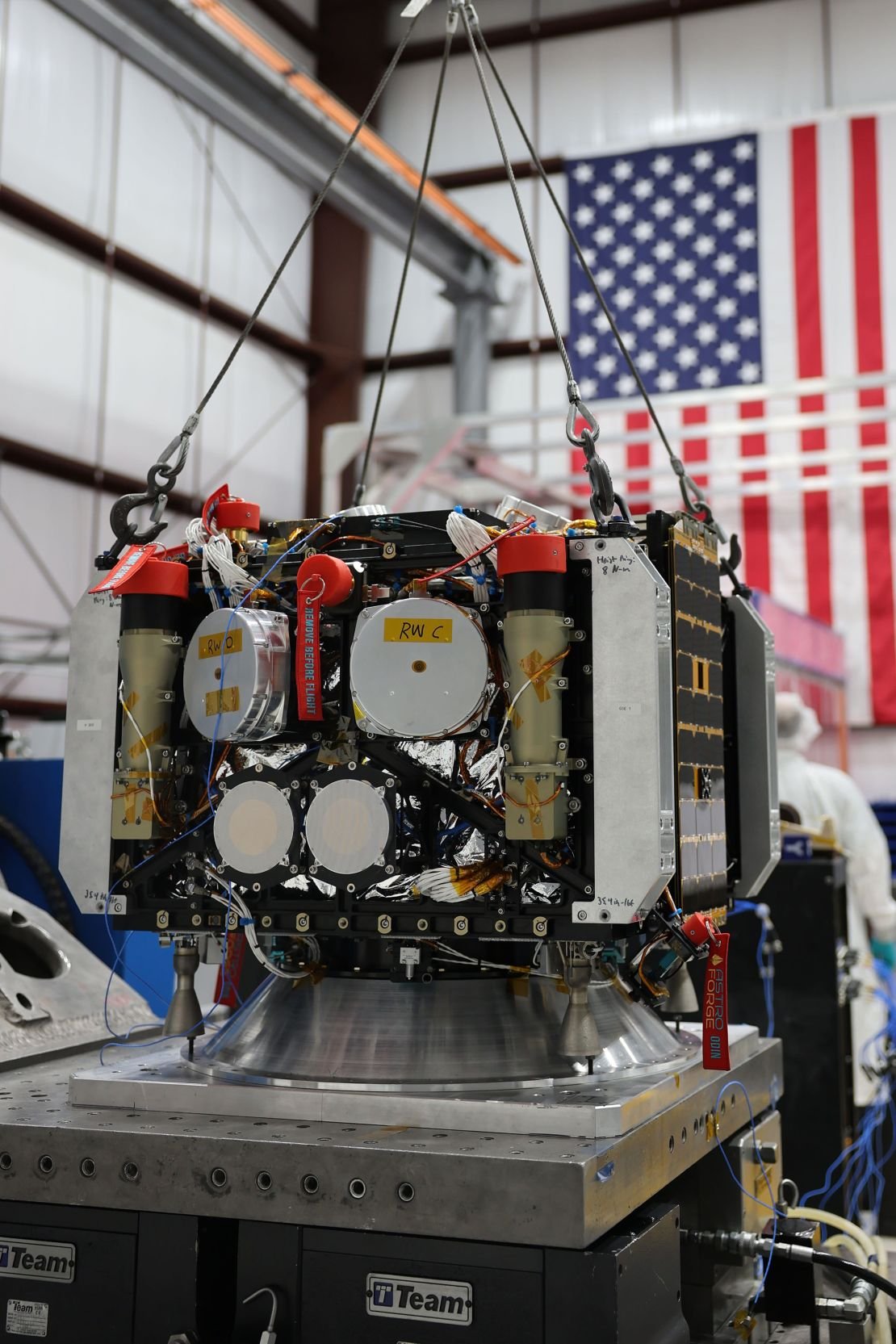
At first, the company publicly refused to say which conflict it would target, and would leave the possibility that the unlawful space could find the unlawful spacecraft. Estrophorez confessed in January after the astronomy community pusback that its purpose is to send the vehicle to a disciple. 2022 OB5 – A relatively smal small space rock that will pass less than 500,000 miles (800,000 km) next year.
But the company’s CEO, Matthew Gileich, told CNN that things could change. “One of the best things we have as a company is that we can change the goals at any time … so it is not a big deal for me to say,” he said.
“Now, when we get this mythology, which is purely platinum and is worth $ 1 trillion – am I going to tell the world which one is it?” “Maybe not.”
National security concerns are another problem that can cloud astronomers’ ability to clearly see the universe, as Dari Norman, the president of the American Astronomy Society, has identified. Line It was published in September, calling for better transparency.
Norman said in the letter, “With the financial support of some US government, the astronomical survey has been restricted to the publication of data … which includes more than 100,000 (kilometers) deep space items.” “This exercise should be reviewed to determine whether there are reasons for national security to implement such restrictions.”
The letter also states that, although a UN resolution requires space firing countries and companies so that they are offering goods where they are offering, the mandate is “big for deep space items Neglect on the scale. ”
The letter states that, with the fact that private companies are launching items at extraordinary rates, is one of the reasons that scientists worry about their current abilities to track the items in our solar system. Are good.
Norman noted in a September letter, “(T) is necessary to promote awareness of the situation in place, reduce interference between missions, to avoid interfering in natural items observations, which potentially There are also observations of the hazardous disciple. ” Outdoor space, including the moon and other heavenly bodies.